This activity outlines the indications, mechanism of action, dosing, significant adverse effects, contraindications, monitoring, and toxicity of gabapentin and increases practitioners’ knowledge about how to approach this medication and all health professionals in how to monitor it to drive better patient outcomes.
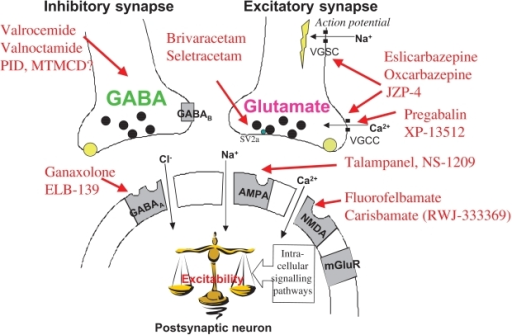
Gabapentin is a prescription medication used primarily to treat certain neurological conditions. Although structurally similar to the neurotransmitter GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid), it does not bind to GABA receptors. Instead, gabapentin works by modulating calcium channels in the nervous system to reduce abnormal nerve activity.
Buy The Cheapest Gabapentin
| Gabapentin 800 mg – 180 Tabs | $199 | free | $199 | Order |
| Gabapentin 600 mg – 180 Tabs | $195 | free | $195 | Order |
| Gabapentin 400 mg – 180 Tabs | $169 | free | $169 | Order |
| Gabapentin 300 mg – 180 Tabs | $159 | free | $159 | Order |
Gabapentin is used with other medications to prevent and control seizures. It is also used to relieve nerve pain following shingles (a painful rash due to herpes zoster infection) in adults. Gabapentin is known as an anticonvulsant or antiepileptic drug.
FDA-Approved Uses
| Indication | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Partial seizures | As adjunct therapy for adults and children (≥3 years) |
| Postherpetic neuralgia | Nerve pain following shingles |
| Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS) | Only the Horizant extended-release form |
OTHER USES: This section contains uses of this drug that are not listed in the approved professional labeling for the drug but that may be prescribed by your health care professional. Use this drug for a condition that is listed in this section only if it has been so prescribed by your health care professional.
Off-Label Uses
Gabapentin is frequently used off-label, meaning for conditions not formally approved by the FDA but supported by clinical practice:
- Neuropathic pain (diabetic neuropathy, sciatica)
- Fibromyalgia
- Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD)
- Bipolar disorder (adjunct)
- Migraine prevention
- Alcohol and opioid withdrawal support
- Hot flashes (in menopause or cancer treatment)
 Gabapentin may also be used to treat other nerve pain conditions (such as diabetic neuropathy, peripheral neuropathy, trigeminal neuralgia) and restless legs syndrome.
Gabapentin may also be used to treat other nerve pain conditions (such as diabetic neuropathy, peripheral neuropathy, trigeminal neuralgia) and restless legs syndrome.
Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic medication, also called an anticonvulsant. It affects chemicals and nerves in the body that are involved in the cause of seizures and some types of pain.
Gabapentin is used in adults to treat nerve pain caused by herpes virus or shingles (herpes zoster).
The Horizant brand is also used to treat restless legs syndrome (RLS).
The Neurontin brand is also used to treat seizures in adults and children who are at least 3 years old.
Use only the brand and form of gabapentin that your doctor has prescribed. Check your medicine each time you get a refill at the pharmacy, to make sure you have received the correct form of this medication.
Gabapentin may also be used for purposes not listed in this medication guide.
How should I take gabapentin?
Take gabapentin exactly as prescribed by your doctor. Follow all directions on your prescription label. Do not take this medicine in larger or smaller amounts or for longer than recommended.
The Horizant brand of gabapentin should not be taken during the day. For best results, take Horizant with food at about 5:00 in the evening.
Both Gralise and Horizant should be taken with food.
Neurontin can be taken with or without food.
If you break a Neurontin tablet and take one half of it, take the other half at your next dose. Any tablet that has been broken should be used as soon as possible or within a few days.
Measure liquid medicine with a special dose-measuring spoon or medicine cup. If you do not have a dose-measuring device, ask your pharmacist for one.
If your doctor changes your brand, strength, or type of gabapentin, your dosage needs may change. Ask your pharmacist if you have any questions about the new brand you receive at the pharmacy.
Do not stop using gabapentin suddenly, even if you feel fine. Stopping suddenly may cause increased seizures. Follow your doctor’s instructions about tapering your dose.
Wear a medical alert tag or carry an ID card stating that you take gabapentin. Any medical care provider who treats you should know that you take seizure medication.
This medication can cause you to have a false positive urine protein screening test. If you provide a urine sample for testing, tell the laboratory staff that you are taking gabapentin.
Store at room temperature away from light and moisture.
Store the liquid medicine in the refrigerator. Do not freeze.
How It Works
Gabapentin binds to the alpha-2-delta subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels in the central nervous system. This reduces the release of excitatory neurotransmitters and decreases nerve overactivity, helping with pain, seizures, and restlessness.
Classification
- Drug class: Anticonvulsant / Antiepileptic
- Brand names: Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant (different formulations)
- Controlled substance status: Not a federally controlled drug in the U.S., but some states regulate it due to abuse potential.
Available Forms
- Capsules (100 mg, 300 mg, 400 mg)
- Tablets (600 mg, 800 mg)
- Extended-release tablets (Horizant, Gralise)
- Oral solution
Gabapentin side effects
Get emergency medical help if you have any of these signs of an allergic reaction to gabapentin: hives; fever; swollen glands; painful sores in or around your eyes or mouth; difficulty breathing; swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Report any new or worsening symptoms to your doctor, such as: mood or behavior changes, anxiety, depression, or if you feel agitated, hostile, restless, hyperactive (mentally or physically), or have thoughts about suicide or hurting yourself.
Call your doctor at once if you have:
- increased seizures;
- fever, swollen glands, body aches, flu symptoms;
- skin rash, easy bruising or bleeding, severe tingling, numbness, pain, muscle weakness;
- upper stomach pain, loss of appetite, dark urine, jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes);
- chest pain, irregular heart rhythm, feeling short of breath;
- confusion, nausea and vomiting, swelling, rapid weight gain, urinating less than usual or not at all;
- new or worsening cough, fever, trouble breathing;
- rapid back and forth movement of your eyes; or
- severe skin reaction — fever, sore throat, swelling in your face or tongue, burning in your eyes, skin pain, followed by a red or purple skin rash that spreads (especially in the face or upper body) and causes blistering and peeling.
Some side effects are more likely in children taking gabapentin. Contact your doctor if the child taking this medication has any of the following side effects:
- changes in behavior;
- memory problems;
- trouble concentrating; or
- acting restless, hostile, or aggressive.
Common gabapentin side effects may include:
- dizziness, drowsiness;
- dry mouth, blurred vision;
- headache;
- diarrhea; or
- swelling in your hands or feet.
This is not a complete list of side effects and others may occur. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
Metabolism & Elimination of Gabapentin
🔬 Metabolism and Elimination of Gabapentin
Gabapentin has a unique pharmacokinetic profile compared to many other neurological drugs. Here’s a focused breakdown:
🧪 Metabolism
- Gabapentin is not metabolized by the liver.
- It does not undergo hepatic metabolism (unlike many other antiepileptics or pain medications).
- No involvement of cytochrome P450 enzymes, making it:
- Less likely to cause drug–drug interactions
- Safe for patients with hepatic impairment
🚽 Elimination
| Pathway | Details |
|---|---|
| Primary route | Renal excretion (through the urine) |
| Excreted as | Unchanged drug (no active or inactive metabolites) |
| Half-life | ~5 to 7 hours (in healthy adults) |
| Clearance influenced by | Kidney function (creatinine clearance) |
🧓 Special Considerations:
🩺 In Renal Impairment:
- Reduced clearance → leads to drug accumulation
- Dose adjustment is essential in patients with:
- Chronic kidney disease (CKD)
- End-stage renal disease (ESRD)
- Gabapentin is removable by dialysis (hemodialysis patients may need supplemental dosing)
🔁 In Hepatic Impairment:
- No dose adjustment required, since the liver plays no role in its metabolism.
📈 Clinical Implications:
| Advantage | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Minimal drug interactions | No P450 involvement = safer in polypharmacy |
| Predictable elimination in healthy kidneys | Simplifies dosing and monitoring |
| Safer in liver disease | No liver metabolism = preferred in hepatic impairment |
For more gabapentin inormation, please go to http://www.rxlist.com/neurontin-drug.htm